Discusses application of motivational theories and transformational leadership to the generational behavior of Millennials
Motivating the Millennials
A Generation can be defined by the changes in the common behavior of its populace when compared with its predecessors. It is normally assumed that each generation comprises of individuals born in span of 15-20 yrs, with some born within generational boundaries exhibiting characteristics of both generations. This implies that it’s very likely that in an organizational pyramid, there exist roughly 2-3 generations of workforce at different hierarchies. When managers and subordinates have different attitudes & beliefs, there is bound to be some generational collision that can result in dissatisfaction in the work environment. Motivation depends upon the understanding the needs and aspiration of the subjects; generational collision acts as an intrinsic blocker to the process.
To understand any generation, it is important to understand what causes a generational behavior, however depending upon the geo-political location, it might get redefined. Millennials are most often defined with respect to children born in United States between 1981 and 1999. This definition might not hold in other region and countries, but since there are an ever increasing number of multi-national organizations, it is more reliable to focus on fundamentals of generational behaviors.
Generational Attributes and Behavior
A generation represents a collective behavior of individuals belonging to certain age group and can be studied based on the common attributes that influence or shape the generational behavior. ( See ‘Individual behavior in Organization’)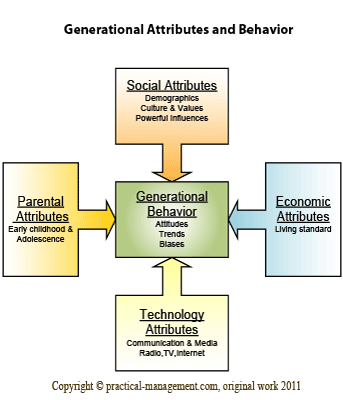
Social Attributes
- Demographics: These are changes in the population compared to previous generation and comprises of factors like changes in race, gender, religion, health & diseases etc. Demographical changes influences the social system in form of public policies, cultural trends etc. As an example, a sudden rise in population after WWII resulted in highly competitive baby boomers in US.
- Culture & Values: Demographics, politics, technology and other influences constantly change the culture of a generation and also its values. Changes in the population of minorities or immigrants might influence the politics and public policies, while integration of other groups in the society results in cultural shift.
- Powerful Influences: The famous people in every generation act as role models and are trend setters. Similarly influential incidents like wars, natural calamities, technological feats etc also influence the culture and acceptable norms.
Parental Attributes
- Size: The number of children represents the span-of-control for the parents, more children implies lesser parental attention. Fewer children imply that more time & resources are being spent on each child; the parent-child relationship is less authoritative and more participative.
- Working mothers: When mothers are working full-time or part-time, their role is shifted from primary caregiver to that of secondary bread earner. When primary caregiver is other than mother, the children tend to be more independent & confident and like to be treated equally, more like adults.
- Married Vs Divorced Parents: Married parents provide a stable, comfortable and predicable environment that nurtures a long term sense of trust & loyalty towards institutions. On the contrary, children of single or divorced parents are skeptical of institutional purpose and tend to rely more on their instantaneous gut feelings in their decision making.
Economic Attributes
- Living standard: Conditions of growing economy shifts the demographics from poverty to middle class where basic necessities are met and preferences shifts towards more meaningful aspects of life. It implies that more resources are being invested in education and other child rearing activities. The natural bias shifts from using coercive ways of self fulfillment to collaborative and competitive attitude.
Technology Attributes
- Communication Technology: Among all innovations, use of technology for communication has the greatest impact on the young generation. Technology determines both the speed by which the information can be delivered, its extent of distribution and its reach to remote population. It can be broadly divided into two categories: Broadcast – like radio, TV, newspaper etc and Interactive- like internet & phone. While broadcast systems are good for delivering facts & news about influential places, people or events, interactive media creates a network of people who can in real-time exchange opinion & views on the events. Affordability of personal computers in 1980-90s and portable internet devices in current era, has shifted the focus towards interactive systems like blogs, tweets, forums and chats.
Generational Behavior of Millennials
The following is a brief review of generational attributes as observed in the Millennials and their resulting generational behavior.
- Social: The Millennial population is rather stable when compared to their predecessor two generations; however there is an increase in immigrant population and therefore more appreciation of diversity. They have been influenced by incidences of 9/11, war against terrorisms and fear of global warming, yet they have been raised with optimism that they can collaborate and fix the future.
- Parental: Millennials had fewer siblings and with relatively stable divorce rates and had better parental attention. Thus they do have better trust on institutions with lesser skepticism. Their inclination towards sex & drugs has also stabilized making them more productive generation.
- Economy: Due to better economy & stable home environment, Millennials have participated in various childhood activities like sports & music lessons, academic daycares etc. They have learnt to work in teams and have been trained to view work as fun. They are more likely to seek gratification in seeking different careers in their life for sake for fulfilling experiences.
- Technology: Millennials are the first truly digitally connected generation, possibly due to wide availability of affordable handheld internet connected devices and applications. Unlike previous generation that relied on emails & phone conversations, the millennials like to be connected to their peers in real-time. Older generation might not understand the importance of social networks and might view this as nuisance, but the millennials are comfortable with virtual presence on the social network. The digital mobile platform has become the primary medium of information exchange from news, books, events, emails and personal communication. This has made them more informed and inquisitive, the faster pace of information has made them seek instant gratifications, and thus they expect to be appreciated rather immediately after finishing an assigned task.
Leadership Motivational Strategies
Most of the text & actual practices about motivational strategies have been formulated as a process that uses some form of rewards, punishment, positive/negative reinforcement and goal setting as a way to motivate employees. A process, by its very definition implies controlling the behavior for the desired outcome. However, technological evolution is creating tasks that are more complicated, less predictable, requires more educated and skill workers who need to collaborate together to produce the complex modern products. All this creates a need to study the importance and feasibility of using leadership as a motivational tool for the newer generation of employees starting from millennials.
In the following section, I have attempted to differentiate motivational theories based on leadership styles. Both extrinsic motivation and transactional leadership (and its predecessors) are short term strategies which can produce deterministic outcomes. They are effective tools in controlling a crisis situation or incrementally leading to a long term solution. On the other end, intrinsic motivation and transformational leadership are form of long term strategies that have a profound impact on how the employees value their association with the organization.
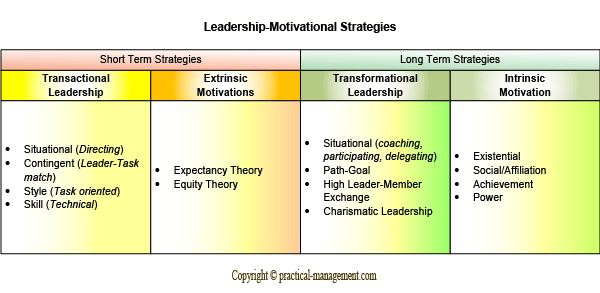
Transactional leadership’s influence on extrinsic motivation
- Transactional leaders utilize contingent reward or punishment to directly influence the employee’s expectancy of the job’s outcome. They negotiate to create short term but achievable goals that individual employee might value, thereby extrinsically motivating the employee. It is commonly observed that when employees are given a clear achievable goal, they tend to work tirelessly till the task completion. The following are important facts that should be considered when designing the rewards:
- Rewards should be something the employee values and considers it at par with that received by his peers (equitable).
- The goals should be specific and not vague, they must not be intentionally difficult or beyond employee’s abilities.
- Rewards have very short term productivity benefit, the motivation drops once the task is completed. Excessive rewards undermines the value of intrinsic motivation like pay, good work, etc and creates a culture where rewards become a necessity for motivation.
- Rewards discourage risk taking and out-of-box thinking, it create a game culture where the focus is rewards.
- Task oriented leadership styles are particularly helpful when the developmental level of the employee or team is low and methodical time bound training is critical. For a short duration, task oriented leaders help in reducing the effort of the employee while improving the outcome, thereby raising the perceived equity (Equity Theory).
Transformational leadership’s influence on intrinsic motivation
Transformational leaders create a synergic organizational environment where both leaders and subordinates work towards organizational goals in unison. Transformational leaders utilize their charismatic qualities and render a vision for the organization that intrinsically adds meaning to the goals, they create an environment or culture that encourages being part of the organization and boosts loyalty. In a way, transformational leaders tend to uplift the components of intrinsic motivation in the following ways:-
- Provide a competitive compensation & benefit structure to satisfy the existential needs.
- Create an open and collaborative organization culture that nurtures collective potential and nurture employee development. They create an environment where employees begin to value their association and loyalty to the organization.
- Transformational leaders depict themselves as the agents of employee development; they use different leadership skills to achieve the goals. Depending upon the developmental level of the subordinates, they would coach, openly discuss or participate and delegate the responsibilities & decision making (situational leadership). They would take appropriate steps to assist and remove obstacles to make them more productive (path-goal) and continuously work towards engaging more employees in being part of the organizational citizenship ( High LMX).
How to motivate the Generation Y - the Millennials?
The procedure of determining the generational attributes and behavior described in previous section, combined with concept of leadership models for motivation, provides an insight into what might motivate the millennial generation.
- Work Environment: Millennials are motivated by challenging work that satisfies more than their existential needs. In general, every new generation is more learned & skilled than their predecessor; also the products are getting increasingly complex, often integrating different technological fields into one. Fortunately, Millennials have been raised in a way that encouraged team work, collaboration and a belief that power of many is greater than that of a few. Unlike, their predecessor – Gen X, they are better team player than individual accomplishers, they cherish diversity and believe that there is a proper place and value for every individual in organizational system.
- Management Style: Millennials would prefer more to be lead than managed; the shift is towards transformational leadership style from rather controlling transactional leadership. It should be note that previous style has been heavily concentrated by methods of controlling all aspects of employee productivity; the future is moving towards more balanced approach and doesn’t imply total lack of control.
Millennials have been mentored throughout their childhood, but in a participative manner. They prefer their managers to be team leader s rather than controlling bosses. While all the previous generations considered it normal to perform the assigned task without questioning the authority, millennials like to know the reason or purpose of the task. - Rewards: Millennials would seek more responsibilities and decision making power as preferred rewards. Although this doesn’t undermine the importance of pay equity, but only stresses that this generation tends to move higher in their motivational needs hierarchy.
- Performance: Millennials are digital generation which seeks interactive experience and are used to getting frequent and timely responses/ feedbacks. They would like to receive continuous feedback about their job performance and career development. The web2.0 era along with digitally networked infrastructure has produced new sources of communication & information mediums. The companies like Linkedin, facebook, glassdoor, wikileaks etc have created a new forum of transparency which assists in determining pay, skill and position equity amongst the peers (equity theory). This is a major shift from secretive & closed performance and pay processes that had existed till now. Unfortunately, the Gen X which forms most of the existing management layer is inexperienced, unaware in these tools, or has outright rejected them as mere noise. There is enough of research that supports the idea of not having unreasonable pay difference between different hierarchical levels for a better collaborative culture and this will become more prominent in the future.
Quick tips
- Embrace digital era and use it as an organizational tool.
- Take the responsibility to mentor and coach the millennials.
- Encourage team work and collaboration, be a team leader.
- Maintain high degree of equity and transparency in the decision making and benefits.
